만성 골수성 백혈병에 대한 nilotinib vs imatinib의 장기 임상효과 비교 :
5년 RCT 연구를 통한 업데이트
Long-term benefits and risks of frontline nilotinib vs imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: 5-year update of the randomized ENESTnd trial

그림 1) CONSORT Diagram for ENESTnd 5-Year 분석: Source: doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.5.
[근거기반 임상질문 답변 : SUMMARY)
|
임상질문
|
새롭게 진단받은 만성 골수성 백혈병(Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Chronic Phase, CML-CP) 환자에게 Nlotinib vs Imatinib 치료의 장기효과와 위험요인을 비교하였을 때 차이가 있습니까?
|
|
근거기반 답변
|
Nilotinib는 CML-CP 환자의 일차치료(frontline therapy)로서 하루 두번 300mg 복용 할 경우, imatinib 복용보다 긍정적이고 의미있는 임상 장기 효과를 보고하였다.
|
|
서지정보
|
Long-term benefits and risks of frontline nilotinib vs imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: 5-year update of the randomized ENESTnd trial. Leukemia. 2016 May;30(5):1044-54. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.5.
|
|
연구목적
|
만성 골수성 백혈병 환자에게 Nilotinib과 Imatinib 의 임상 안정성 및 위험 비교
|
|
연구설계
|
Evaluating Nilotinib Efficacy and Safety in Clinical Trials-Newly Diagnosed Patients (ENESTnd) Study, Phase 3
|
|
연구대상
|
6개월 이내 CML-CP 진단을 받았고 이전에 CML 치료를 받은 적이 없는 환자 (N=846)
|
|
시험군 중재
|
Nilotinib 300 mg twice daily (n=282), or Niotinib 400 mg twice daily (n=281)
|
|
대조군 중재
|
Imatinib 400 mg once daily (n=283).
|
|
평가지표
|
MMR, molecular response 4 (MR4; BCR-ABLIS?0.01%);
Molecular response 4.5 (MR4.5; BCR-ABLIS?0.0032%);
Progression to accelerated phase/blast crisis (AP/BC);
Event-free survival (EFS);
Progression-free survival (PFS);
Overall survival (OS);
Safety
|
|
주요결과
|
5 Year Outcomes: 5년 후 MMR결과는 Nilotinib 300-mg 하루 두번 복용군 (n=217, 77.0% 95% CI, 71.6–81.7%), Nilotinib 400-mg 하루 두번 복용군 (n=217, 77.2% 95% CI, 71.9–82.0%)와 Imatinib 400mg 하루 한번 복용군(n=171, 60.4% 95% CI, 54.5–66.2%)를 보고하였음(그림 2 참고), 생존률과 부작용 (그림 3 참고)
|
|
근거수준
|
High
|
|
작성자
|
의과학연구정보센터(MedRIC)
Copyright © 2015. Medical Research Information Center (MedRIC) Editors
|

그림 2) Cumulative molecular response rates. Cumulative proportion of patients with (a) major molecular response (MMR; BCR-ABLIS?0.1%), (b) molecular response 4 (MR4; BCR-ABLIS?0.01%) and (c) molecular response 4.5 (MR4.5; BCR-ABLIS?0.0032%). P values vs imatinib are nominal. IS, International Scale.
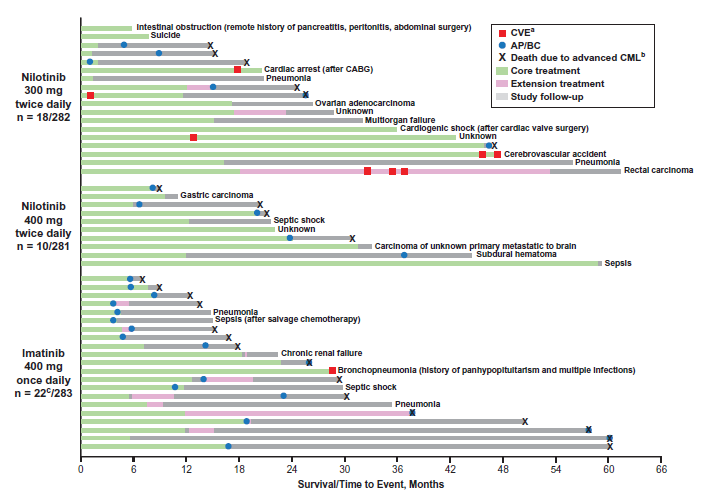
그림 3) Summary of deaths on study by treatment arm. A. The presence/absence of cardiovascular events (CVEs) was collected during treatment (core or extension) only. B. Death due to advanced chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) was defined as any death for which the principal cause was reported by the investigator as ‘study indication’ or, if subsequent to documented progression to accelerated phase/blast crisis (AP/BC), any death for which the cause was reported as ‘unknown’ or was not reported. C. One patient randomized to imatinib who died prior to receiving treatment is not shown. CABG, coronary artery bypass grafting.
출처 :
Long-term benefits and risks of frontline nilotinib vs imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: 5-year update of the randomized ENESTnd trial. Leukemia. 2016 May;30(5):1044-54. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.5.
Nilotinib versus imatinib for the treatment of patients with newly diagnosed chronic phase, Philadelphia chromosome-positive, chronic myeloid leukaemia: 24-month minimum follow-up of the phase 3 randomised ENESTnd trial.Lancet Oncol. 2011 Sep;12(9):841-51. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70201-7.